Off-site Prefabrication Systems
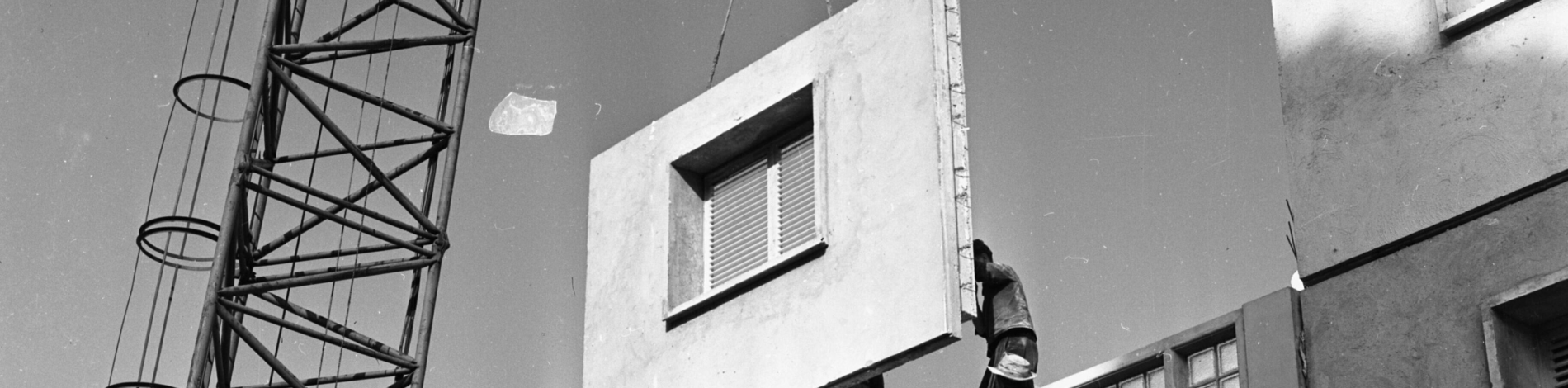

Developing and testing off-site prefabricated systems through full-scale retrofits and new construction experiments.
Context
Off-site construction holds promise to address key challenges of our times.
Off-site construction is experiencing a resurgence after decades of relative stagnation. This is because if offers clear advantages over on-site construction techniques. Applying manufacturing principles to architecture has the potential to play a critical role in meeting housing, skilled labour, and environmental challenges in the architecture, engineering and construction industries.

Prefabricated panels are critical to scaling up deep energy retrofits.
Benefits of off-site fabrication:
Off-site fabrication allows shortens overall timelines and reduces the severity and duration of on-site disturbances.
The centralized and controlled factory setting enables efficient material use.
The controlled factory setting and workflow shelters workers from much of the discomfort and safety risks inherent to the job-site.
Many prefabrication tasks can be automated, re-structured, or supported so as to reducing the volume, skill and physical strength required of the labour force. This can create opportunities for a more diverse workforce.
Opportunities
Controlled conditions in the factory create novel opportunities for envelope component production
Prefabricated panels can serve both to retrofit and to densify the existing building stock.
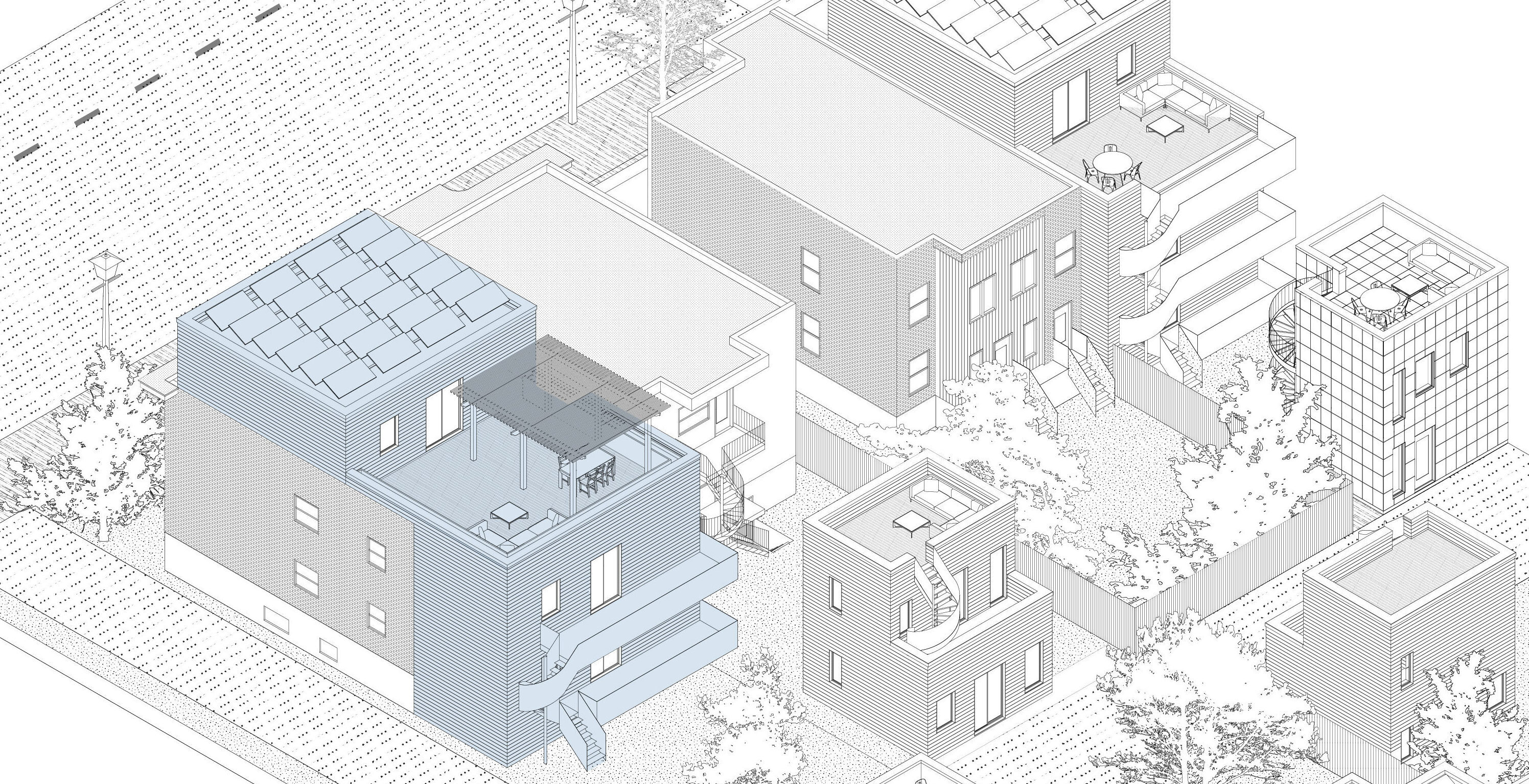
Hybrid panelized retrofit & densification strategies applied to common Montreal building types.
Panelized retrofits
In retrofits, a panelized over-cladding approach enhances the thermal insulation and airtightness of the building envelope. This reduces the building's heating & cooling demands so that it can use ultra-high efficiency active systems. The resultant buildings have several proven non-energy benefits (NEB) such as greater resilience, superior Indoor air quality, improved comfort which all contribute to a healthier urban environment. This approach dramatically reduces on-site construction time and minimizes disruptions to occupants and relocation expenses.
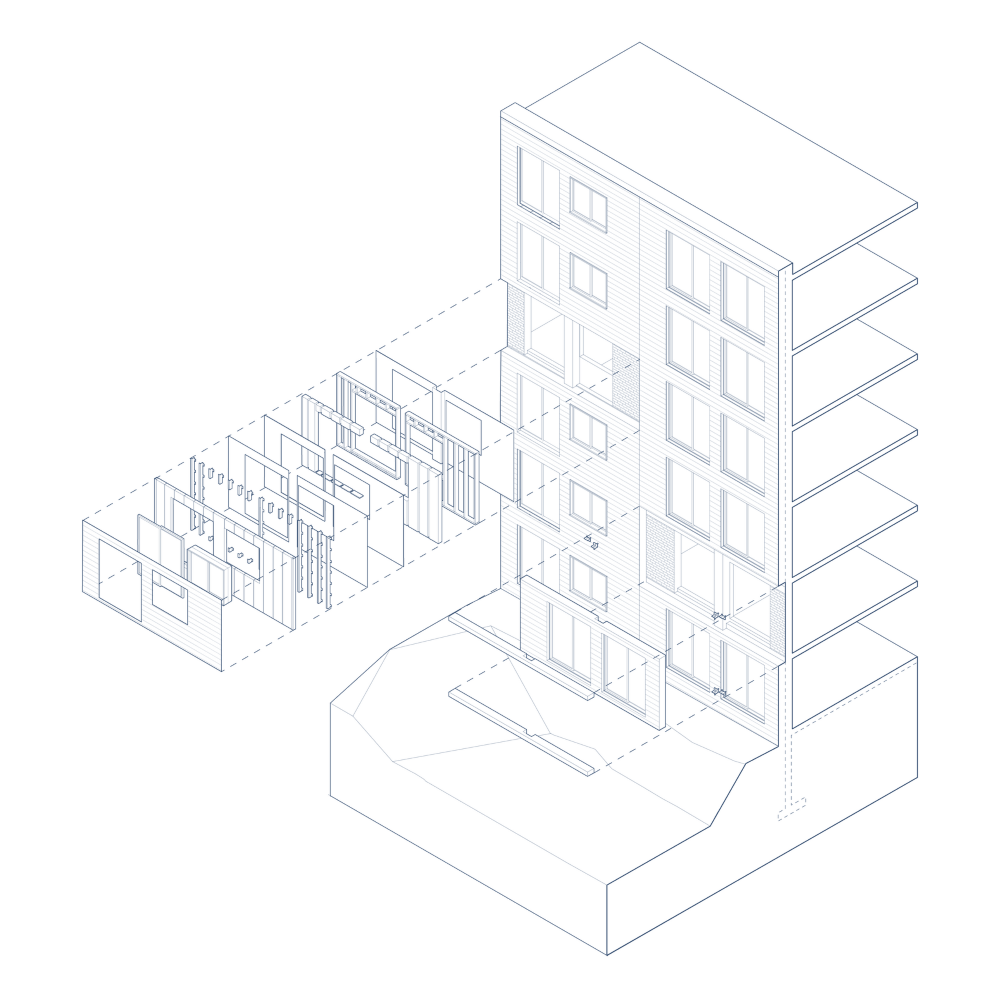
Case study for the panelized retrofit of a non-combustible multi-unit residential building.
Hybrid new/retrofit for densification
Hybrid approaches combining retrofit and new construction can take advantage of densification opportunities. This can facilitate the addition of new panelized dwelling space through extensions, additional stories, and accessory dwelling units (ADUs).
Outlook
Panelized techniques applied to both new construction and adaptive reuse can play a key role in redefining architectural intervention in the built environment and meeting interrelated challenges of building and maintaining resilient communities, addressing climate change mitigation and adaptation imperatives, as well as the housing crisis.
Our pilot projects
The Île-Bizard-Sainte-Geneviève Community Centre
Discover our pilot projectThe Île-Bizard Community Centre, which plays a crucial role as both a neighborhood hub and an emergency shelter, is the focus of a pilot project aimed at a holistic upgrade to its energy performance

Discover Our Collaborators






- Arrondissement de l’Île-Bizard—Sainte-Geneviève
- Société d’habitation du Québec
- Building decarbonization alliance
- Pembina institute
- Québec BVI – Bâtiment vert et intelligent
- ReCover Initiative
- Retrofit Canada
- The Atmospheric Fund (TAF)
- Transition Accelerator
- Zero Emissions Innovation Centre
- If Then Architecture Inc.
- Minotair Inc.
- RG Solutions
